CCI – Central Plant Controller
Align your power plant to the CEI 0-16 V1 and V2 regulations thanks to our CCI
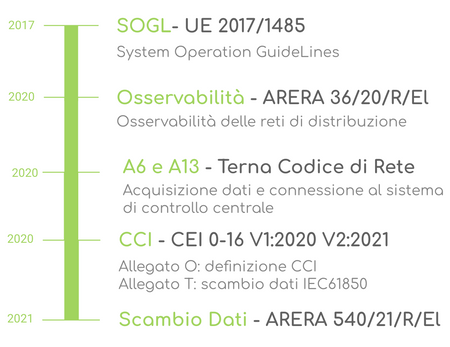
The European Guideline for electricity transmission system (SOGL) establishes the importance of monitoring and controlling distributed generation (DER) and in particular from renewable sources (RES).
In line with new regulations, the Italian regulatory body ARERA entrusts the DSO with the task of acquiring and sending data from production plants to the energy transmission operator (TSO).
The CEI has introduced the Central Plant Controller (CCI) as the V1 and V2 variants in accordance with the standard 0-16. The CCI is installed at the Delivery Point and allows DSOs to monitor and regulate the power production plant, thereby taking part in the balancing of the grid.
Which plants are subject to the CCI
All the production plants with power greater than or equal to 1 MW connected in Medium Voltage (MV)
-
The plants are operational from 01/12/2022
-
The plants operational until 30/11/2022 to be adapted by 31/01/2024
-
The plants connected in medium voltage that participate in the Dispatching Markets of any Pn

CONTRIBUTION TO FACILITATE COMPLIANCE WITH THE LEGISLATION
Economic bonus for CCI
For existing plants, the Authority has provided a flat-rate contribution in order to facilitate compliance with the legislation. The amount of this contribution depends on the date of dispatch of the notice of correction, the checks of which have been successful.
The process includes:
- The manufacturer sends confirmation to the distributor that work has been completed on meeting the CCI compliance;
- The distributor must carry out within two months of confirmation remote checks or sample inspections;
- In the event of a negative result, the manufacturer has 2 months to carry out corrective actions and communicate it to the distributor, who then organises new checks within 1 month;
- In the event of a positive outcome, the distributor disburses the bonus within 3 months of notification of the compliance.
Higeco More answers the most common questions about the CCI
FAQ on the Central Plant Controller (CCI)
For which plants is the CCI mandatory?
The introduction of Resolution 540/21 by ARERA makes the use of the CCI mandatory for production plants with power greater than or equal to 1 MW connected in Medium Voltage (MV). CCI is mandatory for NEW PLANTS and retrofitting for EXISTENT PLANTS according to the following criteria:
- NEW PLANTS: mandatory for all plants that are operational starting 01/04/2023.
EXISTENT PLANTS: all plants that come into operation until 31/03/23 must be retrofitted by 31/05/2024.
For which plant technologies is the CCI mandatory?
There are no distinctions of technology (technology neutrality). The CCI is mandatory for any electricity production plant with a nominal power greater than 1MW and connected in MV.
For which plants is the bonus provided?
Resolution 540/21/R/el establishes the disbursement of an economic bonus, by the DSO, only for plants for which there is an obligation to adjust, i.e. those that became operational before 1 April 2023. The bonus amount is equal to:
- €10,000 for plants that complete the procedure by 31 July 2023
- €7,500 for installations that complete the procedure by 31 October 2023
- €5,000 for plants that complete the procedure by 31 January 2024
- €2,500 for plants that complete the procedure by the last available date, i.e. 31 May 2024
Are there specific measures for plants between 6 MW and 10 MW?
For plants with a nominal power exceeding 6 MW, and connected in MV, there are additional monitoring and control requirements, specified in Annexes K and X of CEI 0-16 2022-03.
For plants connected in AT, refer to the requirements indicated in Attachment A68 of the Grid Code.
What functionality should the CCI have? Are they all mandatory?
Legislation requires 3 functional categories: mandatory, optional and voluntary.
- PF1: The first group refers to mandatory monitoring functions.
- PF2: The optional functions are activated at the discretion of the DSO, are related to the remote control of the system and regulate the voltage and frequency of the network.
- PF3: Voluntary functions are activated at the discretion of the manufacturer and relate to plants in the dispatching service markets and include optimised management of the plant and loading in start-up or reconnection.
Does the CCI need to be connected to the internet?
It better be. Indeed, the CCI must use a PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) for the management of security certificates (see CEI 0-16 T.3.3.4.9).
According to Annex T there are 3 ways to do this:
1 – Manual Management (temporary solution only): Installations, updates, revocations, replacements of the DSO certificates and any BSPs must be done manually on each plant. Challenging and error-prone if there are many CCIs to manage.
2 – Local PKI in the plant and OCSP protocol: Installing and managing a local PKI is very expensive and difficult. It is neither convenient nor safe.
3 – External PKI in the CLOUD: The CCI uses an external PKI in the #cloud, through the internet connection. Secure, centralized and automatic certificate lifecycle management.
Furthermore, a CCI connected to the internet is easier to update – mandatory updates are already foreseen in the coming years – to reach and consult – through our portal – to be replaced in case of failure – automatic backup of configurations and data.
What data should be collected by the CCI?
The CEI 0-16 2022-03 standard requires the following data to be collected:
- Delivery Point: measurement of P, Q, V and optionally I. DG and DI status
- Single Generators: P and DDG status
The CEI standard requires the measurements of the individual generators only if they have a rated power greater than:
- 170kW for static converters (e.g. photovoltaic inverters)
- 250kW for traditional generators
- 50kW for storage
Furthermore, the Arera Resolution 540/21 in Article 2 indicates that the measurements of the individual generators are required only for new plants. For the measurements, the precision required is that indicated in tables 5 and 6 of Attachment A.6 Terna: maximum measurement error less than or equal to 2.2%. For existing single generators only, the maximum error rises to 10%.
How does the CCI control the plant? Are there any requirements?
The control functions of the CCI are based on closed-loop regulators. These regulators read the measurements at the delivery point, compare them with the set points, which are received (slave mode) or calculated (autonomous mode), calculate the set points to be sent to generators/converters and send them. Consequently, the CCI must be able to communicate reliably and quickly with the generators/converters, which must implement a standard communication interface and protocol which provides for the possibility of receiving commands in P and Q (or equivalent, for example PF or PHI ). If the communication is based on serial protocols, such as RS485 or CANBUS, and not Ethernet, it is more difficult to respect the prescribed response times, and it is necessary to evaluate the feasibility case by case.
On existing photovoltaic systems, if the inverters are very old, and/or from bankrupt companies, how can the system be regulated?
Many photovoltaic inverters, even very old ones, were already set up to be regulated by a centralized control system, i.e. they offer a standard communication protocol with registers that can be used to send commands in P and Q (or equivalent). To verify compatibility, you can check the product manual or the document describing its communication protocol. We have been in the PV system control business for almost 10 years, and so far we have only encountered one brand of inverter that was totally uncontrollable.
Who should certify the CCI? Does it have to be done by a third party?
Once all the tests have been carried out and the certifications have been obtained, as described in chapter O.15 of CEI 0-16 2022-03, CCI manufacturers will be able to issue a self-declaration of conformity to the standard, Annexes O and T. The technical file, thus obtained, must be kept for at least 10 years starting from the last date of manufacture of the product and must be kept at the disposal of the control authorities. A third party, accredited for these attachments to the standard, can certify the conformity of the product, as an enhancement to the self-declaration.
What cyber security certifications are required?
Chapter O.15 of CEI 0-16 2022-03 specifies stringent requirements for both hardware and software cyber security. In particular, the use of a cryptographic component capable of detecting and responding to physical tampering is required, certified according to FIPS-140-2 with level 3. Certification to IEC 62443-4-1, according to the scheme, is also required IsaSecure Secure Development Lifecycle Assessment (SDLA), of the CCI production process, and to IEC 62443-4-2, according to the IsaSecure Component Security Assurance (CSA) scheme, of the CCI product.
Can the CCI compliance tests be carried out in any laboratory?
No, the CEI 0-16 Annex O standard requires various tests, which cannot be carried out in any laboratory. To comply with the standard, the product must pass the insulation, EMC, immunity to interference, and climatic tests in an ISO 17025 accredited laboratory, and the functional tests in the presence of an ISO 17065 accredited inspection body.
Once all the tests have been passed, the relative test and inspection reports obtained, and the required certifications obtained, at which point the manufacturer self-declares that the CCI complies with CEI 0-16 Annex O and T. The technical file with all the test reports and certifications, must be kept and kept available for 10 years.
CCI Certifications
CCI Product Brochure
Some of the market players who have trusted the Higeco More solution
Track record












